Digital Camera Image Sensors and Image Sensor Size
 CCD Image Sensor
CCD Image Sensor
The digital camera image sensor captures and processes information about the light that enters the camera through the camera lens. There are millions of light collecting areas on a digital camera image sensor that are called "photosites"
These light collecting photosites are individual picture elements that are better known as "pixels" One million of these pixels are equal to one megapixel.
The light that is captured and filtered at the image sensor's photosites is converted to digital information which is stored in the camera's memory. The stored digital information is then reproduced as the image or "the picture" that you view on your camera's LCD screen.
The whole process is much more complicated than what was just mentioned, but the point of this tutorial is to give you a basic understanding of the function of a digital camera image sensor.
Most consumer cameras use one of the two following types of image sensors.
These light collecting photosites are individual picture elements that are better known as "pixels" One million of these pixels are equal to one megapixel.
The light that is captured and filtered at the image sensor's photosites is converted to digital information which is stored in the camera's memory. The stored digital information is then reproduced as the image or "the picture" that you view on your camera's LCD screen.
The whole process is much more complicated than what was just mentioned, but the point of this tutorial is to give you a basic understanding of the function of a digital camera image sensor.
Most consumer cameras use one of the two following types of image sensors.
 CMOS Image Sensor
CMOS Image Sensor
CCD Sensor (Charge Coupled Device): A CCD Sensor reads the amount and quality of light captured at each photosite sequentially. (one at a time) That information is then transported to additional circuitry in a different area of the sensor where it is converted to digital information.
CMOS Sensors (Complementary Metal Oxide Semi Conductor). Light measurements taken at the photosites in CMOS sensors are processed simultaneously rather than sequentially.
Most of the processing circuitry for converting light to a charge is located at each sensor photosite so that the information doesn't have to be transported to be converted to digital information.This makes for quicker loading and processing of the information about the light.
CMOS Sensors (Complementary Metal Oxide Semi Conductor). Light measurements taken at the photosites in CMOS sensors are processed simultaneously rather than sequentially.
Most of the processing circuitry for converting light to a charge is located at each sensor photosite so that the information doesn't have to be transported to be converted to digital information.This makes for quicker loading and processing of the information about the light.
CCD or CMOS-Which is Better? Both of these sensor types perform the exact same function, but use different techniques for capturing the the light and then converting it to digital information.The differences in their performance are slight.
For instance, CCD sensors have a better dynamic range performance but CMOS sensors use less power. CCD sensors produce images with less noise but CMOS sensors process information faster.
There are other differences, but none that give one sensor a distinct advantage over the other. In other words, the type of sensor should not be only factor in deciding which camera to buy.
Major camera companies like Canon and Nikon primarily use CMOS sensors for their Digital SLR Cameras, while using CCD sensors for most of their Basic Compact Cameras. Just take note that a part of the decisions they make about which sensors to use might have a lot to do with production costs and which type sensors they prefer to market. It's not only about one sensor being so much better than the other.
Although there are differences in the way these sensors operate, at this time, there is not a huge difference in the quality of the final images each type image sensor produces. (especially in the eyes of the average photographer.)
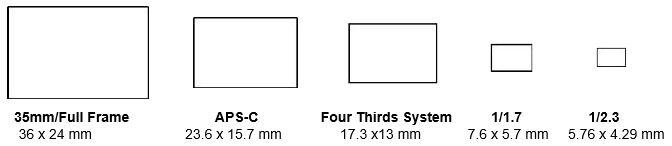
Sensor Size and Pixel Size: Digital camera image sensors are made in various sizes. Most basic compact cameras like the Canon Powershot Elph 190IS use a 1/2.3 size image sensor as shown in the diagram below.
The APS-C sensor is the most commonly used sensor size for consumer level Digital SLR cameras like the Nikon D5600. The APS-C size image sensor is also used in many Compact System cameras. However, some Compact Systems cameras, (also known as Mirrorless Interchangeable Lens cameras) like the Panasonic Lumix DMC-G7 use the Four Thirds system sensors.
These diagrams do not represent actual image sensor sizes. They are for comparison of the sizes only. However, the written numeric dimensions below each one are the actual sizes of each of the image sensors shown.
For instance, CCD sensors have a better dynamic range performance but CMOS sensors use less power. CCD sensors produce images with less noise but CMOS sensors process information faster.
There are other differences, but none that give one sensor a distinct advantage over the other. In other words, the type of sensor should not be only factor in deciding which camera to buy.
Major camera companies like Canon and Nikon primarily use CMOS sensors for their Digital SLR Cameras, while using CCD sensors for most of their Basic Compact Cameras. Just take note that a part of the decisions they make about which sensors to use might have a lot to do with production costs and which type sensors they prefer to market. It's not only about one sensor being so much better than the other.
Although there are differences in the way these sensors operate, at this time, there is not a huge difference in the quality of the final images each type image sensor produces. (especially in the eyes of the average photographer.)
Sensor Size and Pixel Size: Digital camera image sensors are made in various sizes. Most basic compact cameras like the Canon Powershot Elph 190IS use a 1/2.3 size image sensor as shown in the diagram below.
The APS-C sensor is the most commonly used sensor size for consumer level Digital SLR cameras like the Nikon D5600. The APS-C size image sensor is also used in many Compact System cameras. However, some Compact Systems cameras, (also known as Mirrorless Interchangeable Lens cameras) like the Panasonic Lumix DMC-G7 use the Four Thirds system sensors.
These diagrams do not represent actual image sensor sizes. They are for comparison of the sizes only. However, the written numeric dimensions below each one are the actual sizes of each of the image sensors shown.
(note: Canon manufactures their own APS-C image sensor size which measures 22.2 x 14.8 mm)
A full frame sensor is around the same size as the image area on 35mm film. Full frame sensors are usually found in higher end and professional cameras.
As you can see, Compact Camera sensors (eg: the 1/2.3 sensor size) are drastically smaller than the image sensors found in Digital SLR cameras (like the APS-C sensor size).The Compact cameras sensors also have smaller sized pixels than the Digital SLR camera sensors.
A Digital SLR camera with its larger sensor as well as larger pixel sizes, will produce higher quality images than a Compact Digital camera with its smaller sensor and pixel sizes. That is, even if both cameras have the same amount of pixels. For more details about pixels and image quality, read the tutorial, Pixels and Image Resolution.
Images that are taken with larger camera sensors can be enlarged to greater sizes with less loss of image quality than images taken with smaller image sensors. The better image quality is due to the fact that larger size pixels are able to gather more light and information about the quality of the light. Those larger pixels will also produce better images in terms of "noise" and "dynamic range"
Noise is dark or light specs in an image that are more apparent when pictures are taken in lower light settings, and as the ISO (camera light sensitivity) setting is increased. Check the tutorial What is ISO for an example of digital camera noise. Cameras with larger sensors and pixels are able to gather more light, and produce images with less noise in most situations.
Dynamic Range is the ability of the sensor to more evenly capture the highlight (bright) and shadow areas of an image. A larger image sensor will have a better dynamic range than a smaller one.
Generally, the smaller sensors found in compact cameras will produce images that are more than acceptable for the average photographer.However, the more serious photographers who pay more attention to details and want even higher quality in a picture will be better off with a camera that has a larger image sensor.
A full frame sensor is around the same size as the image area on 35mm film. Full frame sensors are usually found in higher end and professional cameras.
As you can see, Compact Camera sensors (eg: the 1/2.3 sensor size) are drastically smaller than the image sensors found in Digital SLR cameras (like the APS-C sensor size).The Compact cameras sensors also have smaller sized pixels than the Digital SLR camera sensors.
A Digital SLR camera with its larger sensor as well as larger pixel sizes, will produce higher quality images than a Compact Digital camera with its smaller sensor and pixel sizes. That is, even if both cameras have the same amount of pixels. For more details about pixels and image quality, read the tutorial, Pixels and Image Resolution.
Images that are taken with larger camera sensors can be enlarged to greater sizes with less loss of image quality than images taken with smaller image sensors. The better image quality is due to the fact that larger size pixels are able to gather more light and information about the quality of the light. Those larger pixels will also produce better images in terms of "noise" and "dynamic range"
Noise is dark or light specs in an image that are more apparent when pictures are taken in lower light settings, and as the ISO (camera light sensitivity) setting is increased. Check the tutorial What is ISO for an example of digital camera noise. Cameras with larger sensors and pixels are able to gather more light, and produce images with less noise in most situations.
Dynamic Range is the ability of the sensor to more evenly capture the highlight (bright) and shadow areas of an image. A larger image sensor will have a better dynamic range than a smaller one.
Generally, the smaller sensors found in compact cameras will produce images that are more than acceptable for the average photographer.However, the more serious photographers who pay more attention to details and want even higher quality in a picture will be better off with a camera that has a larger image sensor.